Overview of Audit Methods
Audit of computers and hypervisors
The following diagram introduces the methods that you can use to audit computers and hypervisors with
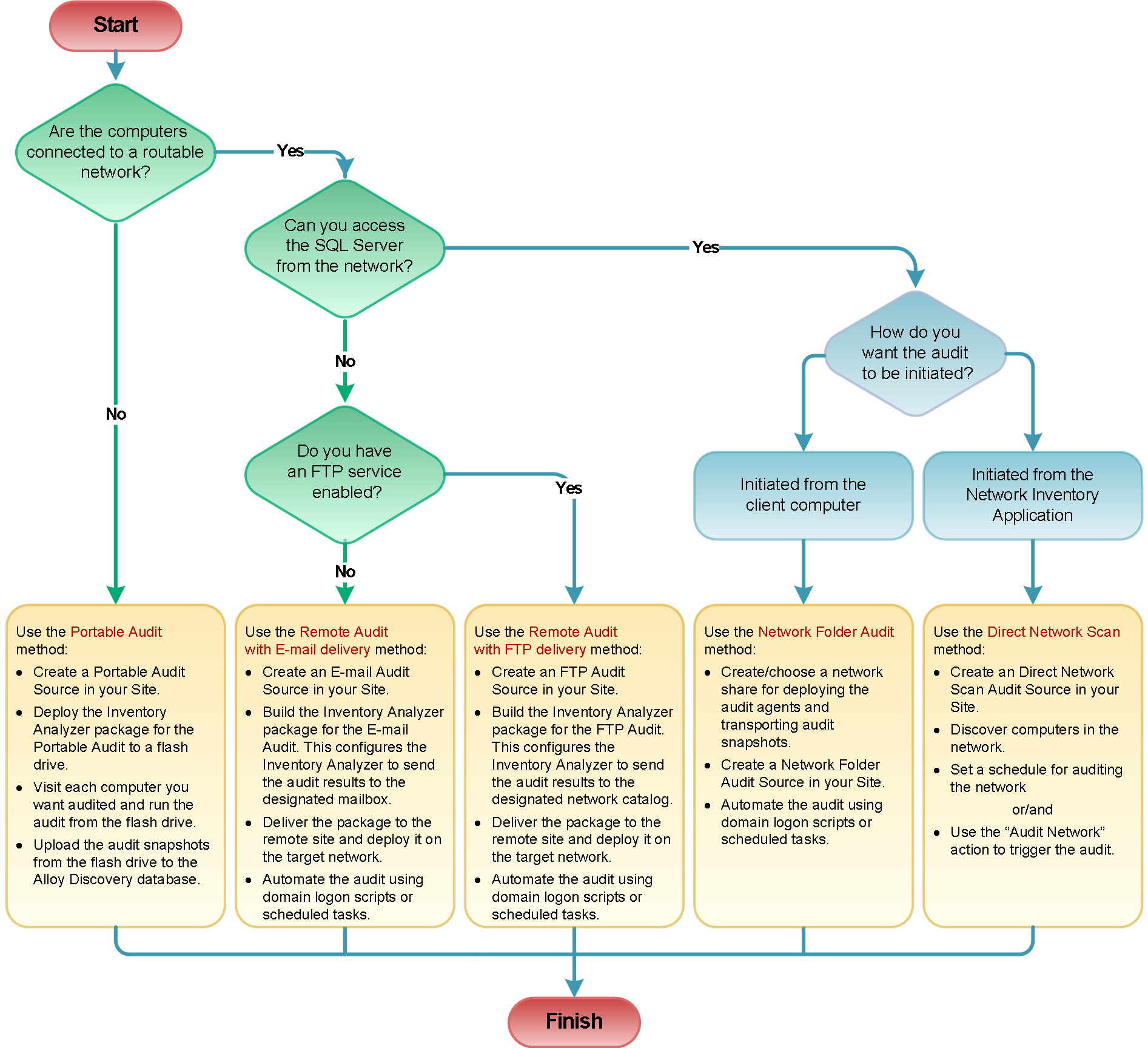
Direct Network Scan
The Direct Network Scan is a method of auditing LAN computers and discovering network devices either at your request or on a regular basis, without the need to deploy standalone audit agents. Built-in audit agents can audit multiple networked computers running Windows, Linux, or macOS simultaneously for up-to-the-minute audit snapshots.
Network Folder Audit
The Network Folder Audit is a method of LAN audit, based on using standalone audit agents. With this method you can audit networked computers on a regular basis. It involves two steps: the deployment of the Inventory Analyzer package to a centralized location, accessible by all networked computers (i.e. a network shared folder), and the automation of the Inventory Analyzer using domain logon scripts or scheduled tasks. Audit snapshots are stored in an intermediary repository on the same network share until they are processed by the
Remote Audit (FTP or e-mail delivery)
The Remote Audit is a method of WAN audit, based on the deployment of standalone audit agents to a remote network. With this method, you can regularly audit offsite computers and remote networks that have no direct connection to the local network.
The Remote Audit method offers two deployment scenarios for audit agents:
- Install the audit agent to every remote computer.
- Deploy the Inventory Analyzer package to a centralized location in the remote network and automate the audit agent using domain logon scripts or scheduled tasks.
Depending on the way how audit snapshots are delivered to
When using the Remote Audit method, there is no direct link between the
Portable Audit
The Portable Audit is a method of auditing computers on locked-down networks and non-networked computers using standalone audit agents. Typically, the audit agent is deployed to a flash drive, which is used to audit individual computers manually. Audit snapshots are stored on the same flash drive and then uploaded into the
Audit of Chromebooks
A Chromebook is a computer running the Chrome OS as its operating system.
The Google Directory Audit is a method of auditing Chromebooks at your request or on a regular basis. When using this method, there is no direct link between the
INFO: For details on configuring G Suite account and Google Admin SDK, see
Audit of network devices