Custom fields for Windows computers
You can expand the default audit data that AlloyScan collects from Windows computers by using PowerShell scripts. This page explains how to create custom fields to collect this additional data. For ready-to-use script examples, see Using PowerShell to collect additional information.
To add a new custom field for Windows computers:
-
On the Custom audit fields page, click
 to start the process of creating a new custom field. The Add new field sliding pane is displayed.
to start the process of creating a new custom field. The Add new field sliding pane is displayed. -
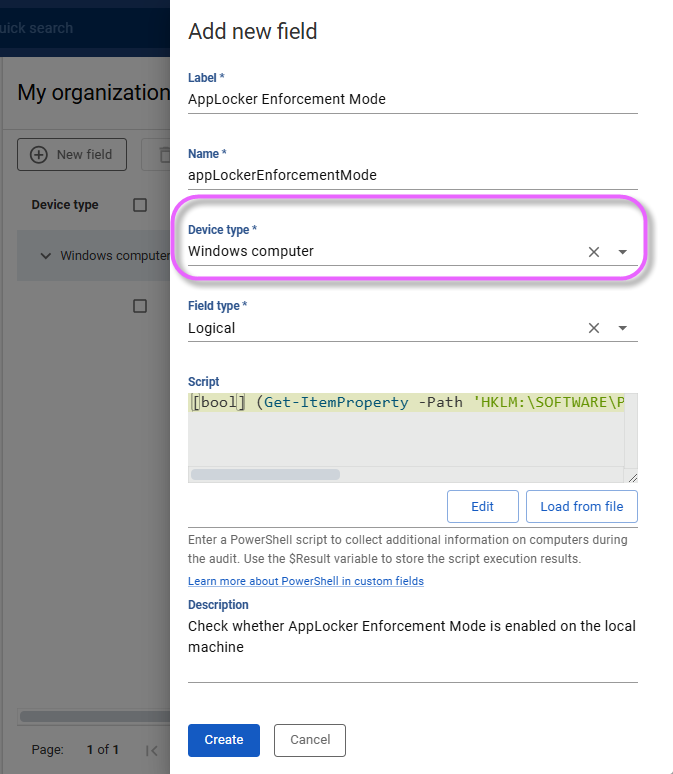
Provide the following parameters:
-
Label: The label for the field, which will be displayed to users during the scanning process.
NOTE: To show a custom field in a shared view (e.g., Inventory data view containing both SNMP devices and Windows computers), use the same label for the matching fields in both device types. See Combining custom fields across device types for details.
-
Name: A descriptive name for the field.
-
Device type: Defines the category of device the custom field applies to. For data collection from Windows computers, this must be set to Windows computer.
-
Field type: Select a data type for the field from the available options, which include Currency, Date, DateTime, Integer, Logical, Memo, String, and Table.
-
Script: Provide a PowerShell script by either editing it directly in the Script Editor or by loading a file. This script will run on every audited computer during the audit and collect additional information. The output must have the same data type as the custom field.
-
Description: A brief explanation of the field's purpose.
-
Once the new custom field has been created, the PowerShell script will run during the audit and the field will store the output for analysis and reporting purposes.
Field data types
AlloyScan currently supports the following data types for custom discovery fields:
-
Currency: A monetary value, such as price.
-
Date: This data type is used for storing dates.
-
DateTime: This data type is used for storing both date and time values.
-
Integer: This data type is used for storing whole numbers, such as the number of CPU cores in a device or the amount of RAM.
-
Logical: This data type is used for storing boolean values, such as true or false.
-
Memo: This data type is used for storing longer blocks of text, such as notes or comments.
-
String: This data type is used for storing single-line character strings, such as the name of a device or software application.
-
Table: This data type is used for storing tabular data.