Configuring Software Licenses
Updated in 2022.1
When you create or modify a Software License record, you set the rules that determine when the license is considered compliant and define the parameters for automatic license allocation. This article describes those rules and parameters.
NOTE: The form that appears when you create a Software License record contains only a limited set of fields. You can specify additional fields later, after the license record has been created.
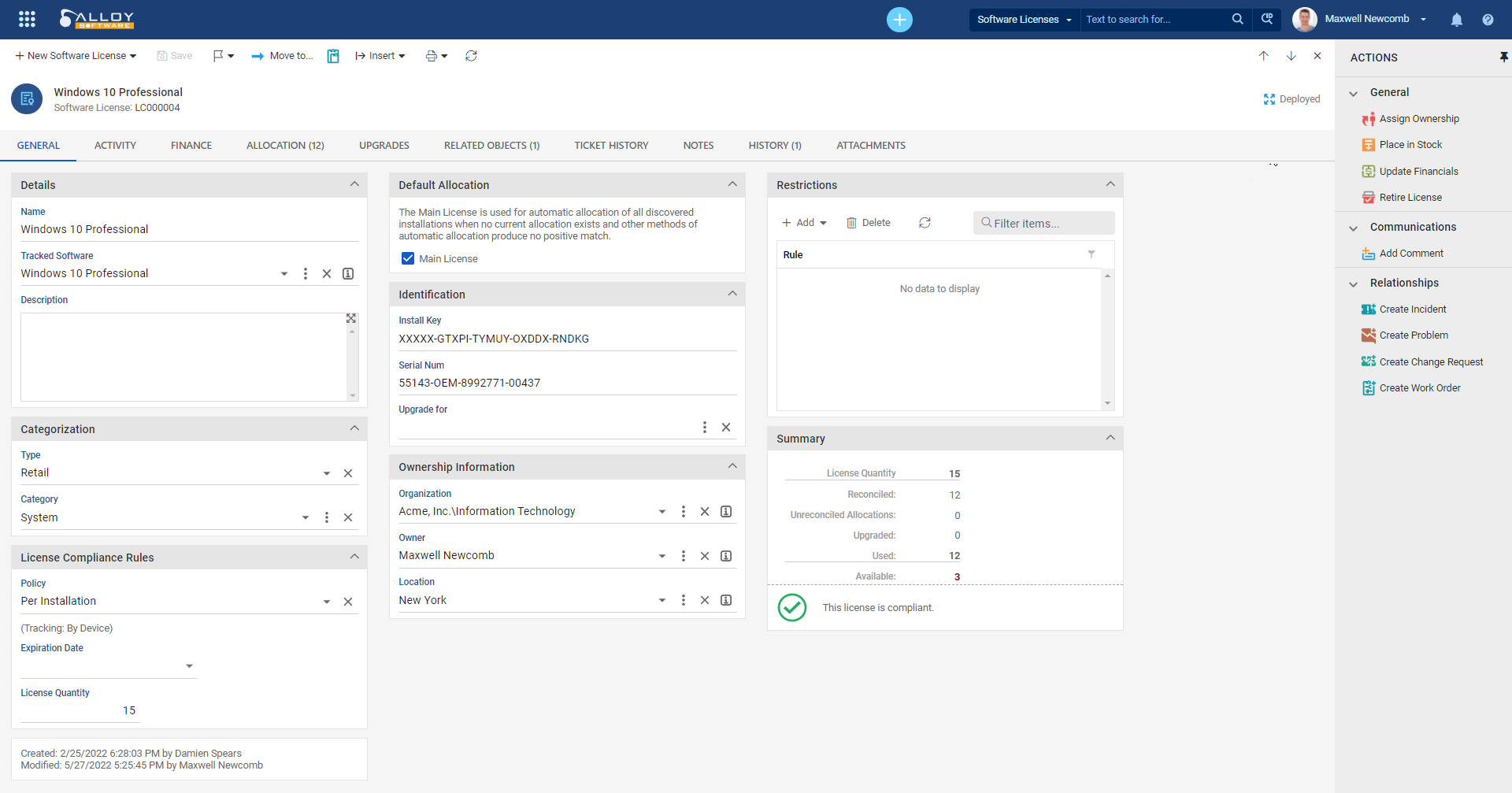
The following Software License parameters define when the license is considered compliant and how Alloy Navigator can automatically allocate it to computers:
-
Install Key — the installation key. This key will be used for auto-allocation of the license. This allocation method works only when the installation key can be detected during the audit. For details, see Allocating Software Licenses.
NOTE: Software manufacturers use the Install Key or the Serial Number to identify software products and individual licenses associated with software installations. Nowadays, most software products use only a Serial Number for license identification. Install Keys are used rarely, typically by older software products.
-
Serial Num — the serial number for automatic license allocation. This allocation method works only when the serial number can be detected during the audit. For details, see Allocating Software Licenses.
-
Upgrade for — denotes an upgrade license, which allows customers who originally purchased an older version of the software to use a newer version of the product. To mark a license as an upgrade license, click the ellipses button and select the original license, i.e., the license for an older software version.
NOTE: Upgrade licenses affect compliance of the original license because each allocation of an upgrade license decreases the amount of allowed installations of the original license. The license goes out of compliance when the total sum of license allocations and allocations of upgrade licenses exceeds the number of allowed installations for the license. For example, you have 100 copies of the original licenses of Microsoft Office 2013 and 20 copies of the upgrade licenses of Microsoft Office 2016. An audit has detected in total 120 product installations of both versions. The license compliance depends on the number of detected installations of Microsoft Office 2016. If it exceeds 20, then the license is non-compliant.
-
Organization — the name of the organization where users are allowed to install the software. If there are detected installations outside the specified organization, the license may become non-compliant. For details, see Policy and Restrictions below. Along with that, the value of this field will be used for the auto-allocation of the license. This allocation method works only when the user company from the snapshot matches the specified license’s organization. For details, see Allocating Software Licenses.
-
Location— the name of the location where users are allowed to install the software. If there are detected installations outside the specified location, the license may become non-compliant. For details, see Policy and Restrictions below.
-
Main License— denotes the license which will be used for the automatic allocation of discovered installations of the respective Software Product when no current allocation exists and automatic allocation methods produce no positive match.
-
Policy — the license policy that defines how Alloy Navigator would check the license compliance.
INFO: For details, see Administration Guide: Managing the Software License Policy Lookup List.
The following policies are typically available:
-
Per Installation — This policy states that respective software requires one license entitlement per every installation. The license remains compliant as long as the number of software installations does not exceed the number of allowed installations (the License Quantity value, see below). If you specify any rules under License Compliance Rules, they will be checked as well. This policy is applied by default to all newly created licenses.
-
Named Computer — This policy states that respective software can be installed only on certain computers. You will need to specify those computers under Restrictions by clicking Add > Restriction by Device Name. Typically, the license remains compliant as long as the product is installed on the specified computers and the number of software installations does not exceed the number of allowed installations. If you specify any other rules under License Compliance Rules, they will be checked as well. For details, see Restriction Rules.
NOTE: If your license uses the “Named Computer” policy, you must add at least one “Restriction by Device Name” rule. Otherwise, the license will be always non-compliant.
-
Site License — This policy states that respective software can be installed within a particular location and/or organization only. You will need to specify the location and organization under Restrictions by clicking Add > Restriction by Location / Organization. The license remains compliant as long as there are no installations detected outside of the specified location or organization and the total number of software installations does not exceed the number of allowed installations. If you specify any other rules under License Compliance Rules, they will be checked as well.
NOTE: In order to check whether a software product is installed within the Organization / Location specified for the Software License, Alloy Navigator compares these values from the license record with the Organization / Location values of the Computer where the product is discovered. Restriction rules, if specified, impose additional considerations on the matching (see description of the “Restriction by Location” and “Restriction by Organization” rules below).
NOTE: If your license uses the “Site License” policy, you must add a “Restriction by Organization” or/and “Restriction by Location” rule. Otherwise, the license will be out of compliance.
-
No License Required — This policy states that no license is required for installations of the respective software. The license with “No License Required” policy is always compliant regardless of any compliance rules specified. You may want to use this policy to temporary disable the verification of the licensing compliance for a particular license.
-
Per User — This policy states that respective software is licensed on a per-user basis. This policy type is frequently used for single-user licenses, that typically can be installed on multiple computers. This license remains compliant no matter how many product installations are discovered, as long as all rules specified under License Compliance Rules are satisfied.
-
Tracking - displays the tracking attribute of the license policy.
-
-
Expiration Date — when provided, this is the date when the license expires and becomes non-compliant unless renewed.
-
License Quantity — the maximum number of license entitlements for the organization based on the license purchase agreement. Typically, the license becomes non-compliant when the total sum of license allocations and allocations of license upgrades exceeds the license quantity (see the description of the Policy field above).
-
Restrictions section — in this section you specify additional restriction rules for the license. To add a rule, click Add and select a rule type. For details, see Restriction Rules.