Audit methods
AlloyScan offers two methods for conducting audits: agent-based and agentless. This article describes the advantages of each method and explains how to choose the most suitable method for the specific network configuration and auditing requirements.
Both methods are visually represented in the diagram below, with detailed explanations provided in their respective sections. You will also find below a comparative table summarizing the differences between the two methods for quick reference.
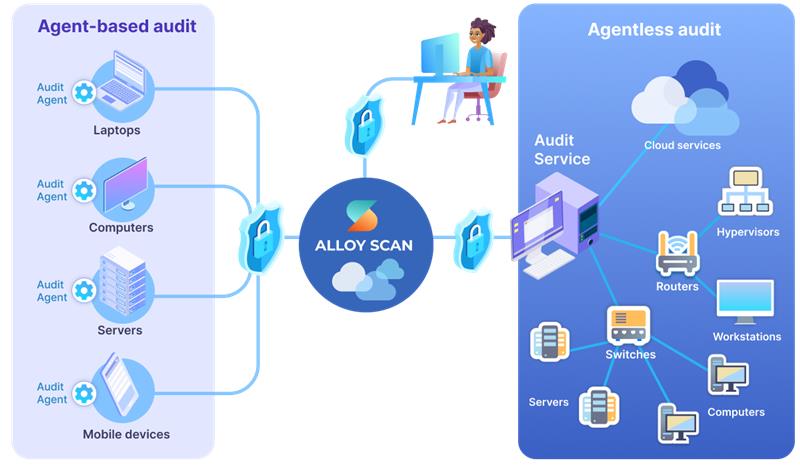
Agent-based method
In the agent-based method, you need to install an audit agent on each computer you want to track. This could include devices such as laptops belonging to remote employees, as well as desktops and servers within the organization's network infrastructure. The agent runs automatically, collecting inventory data and securely transmitting it to AlloyScan.
The agent-based method requires only internet access and outbound HTTPS on port 443 to securely transmit audit data to the cloud service.
Agentless method
The agentless method operates within logical units of your infrastructure, referred to as segments. By designating a single computer within a segment and installing the Audit Service on it, you can initiate network discovery to identify computers, servers, and other network-connected devices such as switches, routers, printers, network cameras, and similar equipment. You can also use this method to discover and audit supported cloud resources. The Audit Service queries supported systems and platforms to collect inventory data and reports the results to AlloyScan.
The agentless method does not require installing agents on individual devices. However, to enable network discovery and data collection, specific ports must be open and certain protocols enabled within the segment where the Audit Service is deployed. For details, see Required ports for agentless audit.
Flexibility and compatibility
You can choose either the agent-based method, the agentless method, or a combination of both, depending on their specific auditing requirements and network configuration. Regardless of the chosen method, the data collected and reported from the audit remains consistent.
| Agent-based | Agentless | |
|---|---|---|
| What IT assets do you want to track? | ||
| Computers: Servers, workstations, desktops, laptops | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Mobile devices: Smartphones and tablets | Planned | |
| Network devices: Routers, switches, printers, network cameras, etc. | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Hypervisors | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Cloud resources: Containters, cloud instances, cloud servers | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Where are the IT assets that you want to track? | ||
| Within the local network: Your office, school, store, etc. | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Within a remote network: An office branch, warehouse, factory, etc. | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Offsite: Remote employees' homes or flexible work locations | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| In Cloud: Azure, AWS, Google Cloud, etc. | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| What platforms do you want to audit? | ||
| Windows | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Linux | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| macOS | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| vSphere/ESXi, Citrix, Xen, Hyper-V | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| iOS | Planned | |
| Android | Planned | |
Watch this quick guided tour to discover the available audit methods and see how to get started with each one.